Pentadecanoic Acid (C15:0): The Next Frontier in Nutritional Science
- Dr. Sean

- Sep 27, 2025
- 4 min read

Disclaimer: This article is intended for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as medical advice.
Introduction: The Search for the Next Essential Nutrient
In the history of nutrition, certain discoveries have redefined human health: the identification of vitamins, the recognition of essential amino acids, and the understanding of essential fatty acids such as omega-3 and omega-6. Today, scientists and industry leaders are beginning to recognize another potential milestone—Pentadecanoic Acid (C15:0).
Once overlooked as a minor component of dairy fat and ruminant meat, C15:0 is now emerging as a promising bioactive fatty acid with unique health benefits and significant market potential. As the global nutraceutical industry searches for innovative, evidence-based ingredients, C15:0 stands out as a candidate worth serious attention and investment.
What Is Pentadecanoic Acid (C15:0)?
Pentadecanoic Acid, abbreviated C15:0, is a 15-carbon saturated fatty acid. Unlike even-chain fatty acids, which are more common in nature, odd-chain fatty acids such as C15:0 have historically received less research focus.
Recent scientific advances, however, have highlighted C15:0 as a potential essential fatty acid—meaning that, like omega-3s, it may be required in small amounts for optimal human health but cannot be synthesized efficiently by the body.
Chemical formula: C₁₅H₃₀O₂
Sources: Dairy products (whole milk, butter), sheep/goat milk, ruminant fat, and certain fish.
Current position: Recognized as a biomarker of dairy intake and increasingly investigated for its functional roles in health.
Scientific Evidence: Why C15:0 Matters

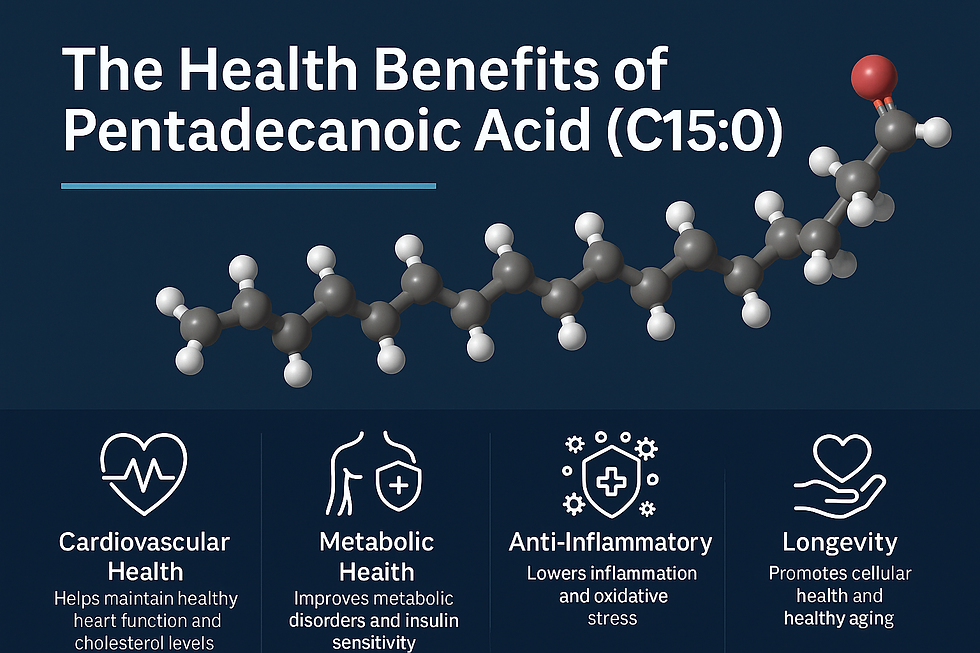
1. Metabolic Health
Studies have shown that individuals with higher circulating levels of C15:0 have a lower risk of metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and fatty liver disease. This suggests that C15:0 plays a regulatory role in maintaining glucose and lipid balance.
2. Cardiovascular Protection
C15:0 is linked to improved lipid profiles and lower markers of systemic inflammation. Unlike industrial trans fats, which harm cardiovascular health, odd-chain fatty acids appear to provide protective benefits.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Emerging preclinical research suggests that C15:0 may help reduce chronic low-grade inflammation, a condition implicated in aging and numerous chronic diseases.
4. Cellular Resilience
Laboratory studies indicate that C15:0 stabilizes cell membranes, enhances mitochondrial efficiency, and reduces oxidative stress, contributing to overall cellular longevity.
C15:0 as “The Next Essential Fatty Acid”
Some scientists have argued that C15:0 should be considered alongside omega-3 and omega-6 as an essential fatty acid. The reasoning is clear:
It is not produced in sufficient amounts by the human body.
Low C15:0 levels are associated with poor health outcomes.
Supplementation has shown promising benefits in cellular and animal studies.
If this classification is accepted, it would open the door for C15:0 to become a mainstream supplement category, similar to fish oil in the early 2000s.
Market Potential: From Dairy Marker to Dietary Supplement
Current Status
Today, C15:0 is primarily recognized in research as a biomarker for dairy fat intake. In nutritional epidemiology, higher plasma C15:0 indicates higher consumption of dairy products, which has been paradoxically linked to lower disease risk despite long-standing concerns about saturated fat.
Future Applications
Dietary Supplements: Purified C15:0 softgels or capsules marketed for metabolic, cardiovascular, and healthy aging support.
Functional Foods: Fortification of dairy alternatives (e.g., plant-based milks) with C15:0 to restore nutritional equivalence.
Sports Nutrition: As a novel fatty acid supporting energy metabolism and recovery.
Healthy Aging Products: Positioning as a longevity nutrient due to its role in cellular stability and inflammation control.
Why the Nutraceutical Industry Should Invest
First-Mover Advantage: Very few companies currently offer C15:0 as a supplement, meaning early entrants can define the category.
Strong Scientific Narrative: The positioning of C15:0 as a “new essential fatty acid” creates a compelling and easily communicated story.
Market Alignment: Fits perfectly with consumer demand for science-based, natural, and preventive health solutions.
Longevity and Wellness Trends: As aging populations drive demand for metabolic and cardiovascular support, C15:0 aligns with high-growth categories.
Regulatory Window: Since C15:0 is naturally present in food, it holds promise for regulatory approval as a safe dietary ingredient in many markets.
Challenges to Overcome
Consumer Awareness: Like omega-3 in its early days, C15:0 will require strong education efforts.
Clinical Evidence: More human intervention studies are needed to confirm benefits.
Supply Chain: Efficient extraction and purification processes must be scaled for commercial demand.
These challenges, however, are typical of emerging raw materials and represent opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
Conclusion: A Strategic Bet on the Future
Pentadecanoic Acid (C15:0) may be a small molecule, but its potential impact on health and the nutraceutical industry is significant. Positioned as a novel bioactive lipid with growing scientific support, C15:0 is poised to follow the trajectory of omega-3 fatty acids—from scientific curiosity to billion-dollar supplement category.
For companies, researchers, and investors seeking the next breakthrough in nutrition, C15:0 represents a forward-looking opportunity worth serious consideration.
In the next decade, we may well see C15:0 transition from an obscure fatty acid to a mainstream essential nutrient, powering innovation in supplements, functional foods, and preventive healthcare.
Disclaimer: The following article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice.












